| Meshing Mode |
Dropdown List |
- This drop-down controls the particle meshing mode.
- See Meshing Modes for more information.
|
| Meshing Mode > Geometry |
List Option |
|
| Meshing Mode > Union Of Spheres |
List Option |
|
| Meshing Mode > Metaballs |
List Option |
- Makes a standard “marching cubes” iso-surface mesh - see Metaballs.
|
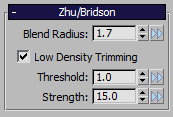
| Meshing Mode > Zhu/Bridson |
List Option |
|
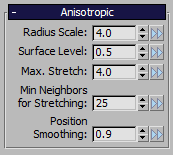
| Meshing Mode > Anisotropic |
List Option |
|
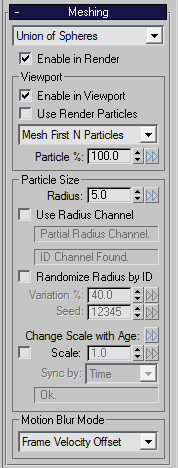
| Enable in Render |
Checkbox |
- Enables mesh creation during rendering.
- When disabled, FROST will produce an empty mesh at render time.
|
| Viewport |
Group |
- Viewport-related Meshing controls.
|
| Enable in Viewport |
Checkbox |
- Controls the mesh creation in the viewport.
- When disabled, FROST will produce an empty mesh in the viewport.
|
| Use Render Particles |
Checkbox |
- Some particle sources generate different particles in the viewport and render.
- When enabled, FROST will use the render particles to create the viewport mesh.
|
| Load Mode |
Dropdown List |
- Controls the order of loading when reading only a fraction of the particles:
|
| Load Mode > Mesh First N Particles |
List Option |
Load particles from the beginning of each particle source until the desired count is reached.
If the particles are ordered (for example saved from geometry primitives, or emitted over time),
this mode will show only a small region that is unrepresentative of the overall shape of the particle cloud,
but since loading just a portion of the file is much faster than reading the whole file,
it was made the default setting.
If the particles in the cloud are completely random (unordered),
the result of this mode will look like the result of Mesh Every Nth Particle but without the speed hit.
|
| Load Mode > Mesh Every Nth Particle |
List Option |
Balance loading through the files, skipping particles to reach the final count.
If the particles are ordered (for example saved from geometry primitives, or emitted over time), this mode
will display a lower particle count that would still represent the overall shape of the particle cloud correctly.
On the negative side, this mode requires each particle object on the current frame to be opened and read
from start to end, making this mode the slower one.
|
| Load Mode > Mesh Every Nth by ID |
List Option |
Balance loading through the files, skipping particles based on the ID channel (if present) to reach the final count.
If every particle has a unique ID, the same particles will be loaded even if other particles are born or die,
resulting in a stable flicker-free particle cloud over time.
This method has the same speed drawback as Mesh Every Nth Particle.
|
| Particle % |
Value Spinner |
- Defines the percentage of particles (first N or every Nth) to be meshed as fraction of the total particle count.
|
| Particle Size |
Group |
- Controls related to the size of the particles.
|
| Radius |
Value Spinner |
- Defines a base particle radius.
|
| Use Radius Channel |
Checkbox |
- When enabled, particles will get their radius from their own radius information.
- Particles that do not have radius information will use the value in the Radius control instead.
|
| Radius Channel Status Indicator |
Text Field |
|
| ID Channel Status Indicator |
Text Field |
- Indicates whether the ID channel is available.
|
| Randomize Radius by ID |
Checkbox |
- When checked, a variation will be added to the size of particles.
- This only affects particles that get their radius from the Radius control.
- The Variation control(see below) controls how much variation is used.
|
| Variation % |
Value Spinner |
- When Randomize Radius by ID is enabled, this is the fraction of the Radius control value that will vary randomly.
- The Maximum Radius is given by the Radius control, the Minimum Radius is (1 - Variation/100.0) * (Maximum Radius).
|
| Seed |
Value Spinner |
- A random seed that is combined with the particle ID to produce random variation.
|
| Change Scale with Age >> |
Menu Button |
- Preset options for changing the size of particles over their lifespan.
- These options set the value of the animated Scale and Synch by controls, below.
|
| Scale |
Checkbox
Value Spinner |
- When checked, the Radius will be multiplied by the Scale to calculate the particle radius.
- The Scale can be animated according to the particle age by using the Synch by control, below.
|
| Synch by |
Dropdown List |
- Controls how an animated Scale is applied to the particles.
|
| Synch by > Time |
List Option |
- The Scale of all particles is animated using the scene time.
|
| Synch by > Age |
List Option |
- The Scale is animated using the Age channel of the particles.
|
| Synch by > Life % |
List Option |
- The Scale is animated using the lifespan percentage of the particles.
- The Life % is 0 at a particle’s birth, and is 100 at its death. This is calculated as 100 * Age / LifeSpan.
|
| Motion Blur Mode |
Dropdown List |
- Controls how the mesh is created for subframes between integer frame numbers.
|
| Mo.Blur > Frame Velocity Offset |
List Option |
- A mesh is created for each integer frame.
- For subframes, the whole frame mesh is offset using the particle velocity.
- This keeps the mesh topology consistent within the half-frame before and after each frame.
- This is necessary for correct motion blur in most geometry renderers incl. V-Ray, mental ray and finalRender.
- See Motion Blur Modes for more information.
|
| Mo.Blur > Subframe Particle Position |
List Option |
- A mesh is created for each subframe.
- This is useful for multi-pass motion blur rendering where topology changes do not matter.
- See Motion Blur Modes for more information.
|